Different Shapes of Sputtering Targets
(주)연진에스텍은 Planar (flat) Target과 Rotary (cylindrical) Target, Circular Target 및 Ring Target 등 대부분의 증착 공정에 부합하는 다양한 형태의 스퍼터링 타겟을 제공하며, 타겟 크기의 커스터마이즈가 가능합니다.
Nickel Ferrite Sputtering Target, NiFe2O4
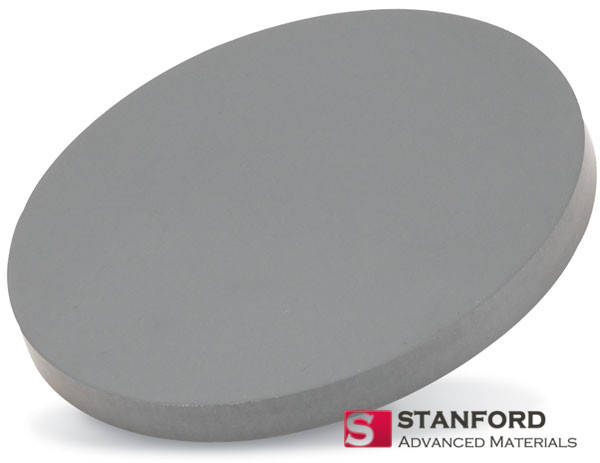

Nickel Ferrite Sputtering Target Description
Nickel ferrite sputtering target from Stanford Advanced Materials is an alloy sputtering material containing Ni and Fe.
Nickel is a chemical element that originated from the shortened of the German ‘kupfernickel’ meaning either devil’s copper or St. Nicholas’s copper. It was first mentioned in 1751 and observed by F. Cronstedt. The isolation was later accomplished and announced by F. Cronstedt. “Ni” is the canonical chemical symbol of nickel. Its atomic number in the periodic table of elements is 28 with a location at Period 4 and Group 10, belonging to the d-block. The relative atomic mass of nickel is 58.6934(2) Dalton, the number in the brackets indicating the uncertainty.

Iron, also called ferrum, is a chemical element that originated from the Anglo-Saxon name iren (ferrum in Latin). It was early used before 5000 BC. “Fe” is the canonical chemical symbol of iron. Its atomic number in the periodic table of elements is 26 with a location at Period 4 and Group 8, belonging to the d-block. The relative atomic mass of iron is 55.845(2) Dalton, the number in the brackets indicating the uncertainty.
Nickel Ferrite Sputtering Target Specification
|
Material Type |
Nickel Ferrite |
|
Symbol |
NiFe2O4 |
|
Color/Appearance |
Gray solid |
|
Melting Point |
N/A |
|
Density |
5.4 g/cm3 |
|
Available Sizes |
Dia.: 2.0″, 3.0″, 4.0″, 5.0″, 6.0″ |
We also offer other customized shapes and sizes of the sputtering targets, please send us an inquiry for more information.
Nickel Ferrite Sputtering Target Packaging
Our nickel ferrite sputter targets are carefully handled to prevent damage during storage and transportation and to preserve the quality of our products in their original condition.
- High Purity & Performance 일관된 증착 품질과 오염을 줄이도록 가공합니다.
- Material Variety 다양한 응용 분야의 요구 사항에 맞게 순수 금속, 합금, 세라믹 및 화합물로 제공됩니다.
- Custom Manufacturing 특정 시스템의 필요요구 사항에 맞게 크기와 형태, 조성을 맞춤화했습니다.
- Precision Design 반복 가능하고 균일한 박막 결과를 위해 엄격한 공차로 제조되었습니다.
- Flexible Supply Chain 최고의 제조업체와 강력한 파트너십을 통해 일관된 품질과 on-time 납품을 보장합니다.
