Different Shapes of Sputtering Targets
(주)연진에스텍은 Planar (flat) Target과 Rotary (cylindrical) Target, Circular Target 및 Ring Target 등 대부분의 증착 공정에 부합하는 다양한 형태의 스퍼터링 타겟을 제공하며, 타겟 크기의 커스터마이즈가 가능합니다.
- High Purity & Performance 일관된 증착 품질과 오염을 줄이도록 가공합니다.
- Material Variety 다양한 응용 분야의 요구 사항에 맞게 순수 금속, 합금, 세라믹 및 화합물로 제공됩니다.
- Custom Manufacturing 특정 시스템의 필요요구 사항에 맞게 크기와 형태, 조성을 맞춤화했습니다.
- Precision Design 반복 가능하고 균일한 박막 결과를 위해 엄격한 공차로 제조되었습니다.
- Flexible Supply Chain 최고의 제조업체와 강력한 파트너십을 통해 일관된 품질과 on-time 납품을 보장합니다.
Molybdenum Niobium Alloy Rotary Target
Molybdenum Niobium Alloy Rotary Target
Description
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) supplies Molybdenum-Niobium (MoNb) alloy rotary targets for thin-film deposition in high-demand environments. The standard alloy contains 90% molybdenum and 10% niobium, combining molybdenum’s thermal and electrical conductivity with niobium’s added mechanical strength and corrosion resistance.
MoNb rotary targets allow for high material utilization (up to 80–90%), which extends target lifespan and reduces production downtime. The uniform grain structure and controlled composition ensure stable sputtering and even coating across large surfaces.
These targets are available in a range of dimensions and can be tailored to fit different sputtering systems. SAM manufactures and inspects each target to meet strict quality and performance standards.
Molybdenum Niobium Alloy Rotary Target Description
Properties
|
Grade |
Density
(g/cm3) |
Average Grain Size
(μm) |
Roughness
(μm) |
Straightness
(mm) |
Bonding Rate |
|
MoNb5 |
≥10.00 |
≤100 |
≤0.8 |
≤0.30 |
≥97% |
|
MoNb10 |
≥9.90 |
≤100 |
≤0.8 |
≤0.30 |
≥97% |
Chemical Composition. %
|
Chemical Composition |
MoNb5 |
MoNb10 |
|
|
Main Content, %, min
Mo |
Mo |
94.85-95.05 |
89.85-90.05 |
|
Nb |
5.00±0.1 |
10.00±0.1 |
|
|
Impurity Content (mass fraction),
%, max |
Al |
0.0050 |
0.0050 |
|
Cr |
0.0050 |
0.0050 |
|
|
Cu |
0.0050 |
0.0050 |
|
|
Fe |
0.0100 |
0.0100 |
|
|
Ni |
0.0050 |
0.0050 |
|
|
Si |
0.0060 |
0.0060 |
|
|
C |
0.0150 |
0.0150 |
|
|
O |
0.0800 |
0.0800 |
|
|
N |
0.0300 |
0.0300 |
|
*The above product information is based on theoretical data. For specific requirements and detailed inquiries, please get in touch with us.
Molybdenum Niobium Alloy Rotary Target Applications
- Flat Panel Displays (TFT-LCD & OLED): Serves as a conductive barrier layer in thin-film transistors.
- Semiconductors & Microelectronics: Used in IC and microchip production for stable, clean film deposition.
- Optical Coatings: Provides durable, conductive, or anti-reflective layers in precision optics.
- Thin-Film Solar Cells (CIGS & PV): Functions as a reliable back contact, boosting efficiency and corrosion resistance.
- Corrosion-Resistant Coatings: Ideal for high-temperature and chemically harsh environments.
Molybdenum Niobium Alloy Rotary Target Packaging
Products are packaged based on size and fragility:
- Small parts: PP boxes
- Larger targets: Custom wooden crates with internal cushioning
Each shipment is packed to prevent contamination or mechanical damage during handling and transport.
Manufacturing Process
1. Brief Manufacturing Process Flow
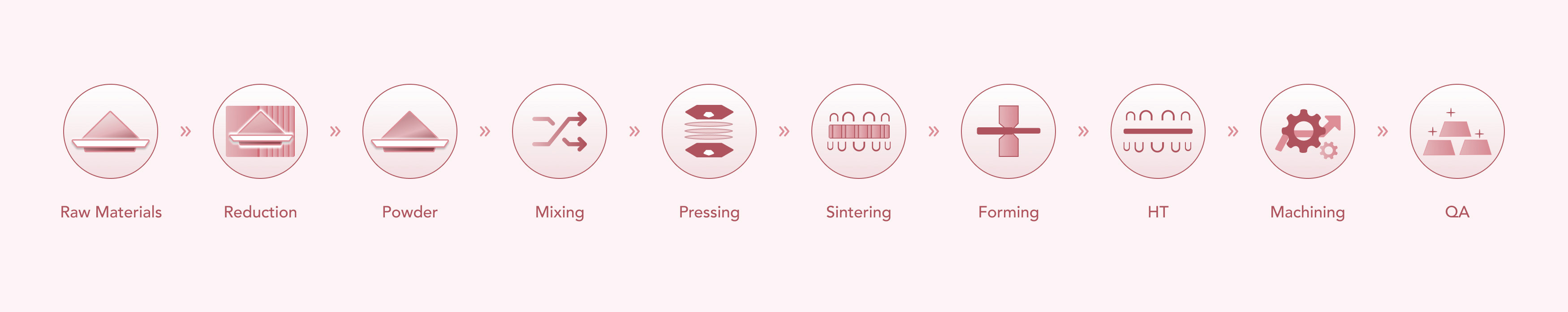
2. Testing Method
-
Chemical Analysis: GDMS or XRF for purity.
-
Mechanical Testing: Tensile strength, yield, elongation.
-
Dimensional Inspection: Ensures specs are met.
-
Surface Quality Check: Visual and ultrasonic inspection for defects.
-
Hardness Testing: Verifies material integrity.
Molybdenum Niobium Alloy Rotary Target FAQs
Q1: Why choose rotary targets over planar?
A1: They use more of the material (up to 80–90%) and last longer, which cuts down on replacements and waste.
Q2: Where are MoNb rotary targets used?
A2: In applications requiring reliable, high-performance films: displays, semiconductors, solar cells, and corrosion-resistant coatings.
Q3: What does niobium add to molybdenum targets?
A3: Niobium improves resistance to oxidation and corrosion, and boosts mechanical durability, especially under thermal and chemical stress.
Performance Comparison Table with Competitive Products
MoNb Rotary vs. MoNb Planar Target
|
Feature |
MoNb Rotary Target |
MoNb Planar Target |
|---|---|---|
|
Material Use |
80–90% |
30–40% |
|
Service Life |
Longer |
Shorter |
|
Coating Uniformity |
Higher, better for large areas |
Less consistent |
|
Cost Efficiency |
Higher initial, lower long-term |
Lower initial, more frequent replacements |
|
Equipment |
Rotary sputtering systems |
Traditional planar systems |
|
Ideal Use |
Large-area coatings |
Small-area, precision coatings |
Material Info: Molybdenum
-
Atomic Number: 42
-
Density: 10.28 g/cm³
-
Melting Point: 2,617°C
-
Thermal Conductivity: 138 W/m·K
Used in electronics, high-temp alloys, energy systems, and as a catalyst in refining.
Material Info: Niobium
-
Atomic Number: 41
-
Density: 8.57 g/cm³
-
Melting Point: 2,477°C
-
Thermal Conductivity: 53.7 W/m·K
Used in superconductors, aerospace, energy systems, and corrosion-resistant equipment.
하기

